Abstract
Diffusion models have recently emerged as a promising paradigm for recommender systems, demonstrating impressive performance in modeling user preferences. However, as with other deep learning approaches, concerns about fairness remain largely unexplored for these models. This paper presents the first comprehensive empirical study on the fairness properties of diffusion-based recommender systems. We investigate how DiffRec and its variants perform across different demographic groups, analyzing both consumer and provider fairness from multiple perspectives.
Motivation
Why study fairness in diffusion recommenders? Diffusion models represent a new generation of recommender systems with state-of-the-art performance. However, their fairness properties are completely unknown. Understanding potential biases is crucial before widespread deployment of these systems.
Methodology
We study DiffRec and its variants, which apply diffusion processes to collaborative filtering. The core idea is to model the user-item interaction generation as a reverse diffusion process:
$\mathbf{x}_t = \sqrt{\alpha_t}\mathbf{x}_0 + \sqrt{1-\alpha_t}\boldsymbol{\epsilon}$
For demographic parity, we measure the disparity in performance metrics between user groups:
$$\text{DP} = |S(G_1) - S(G_2)|$$
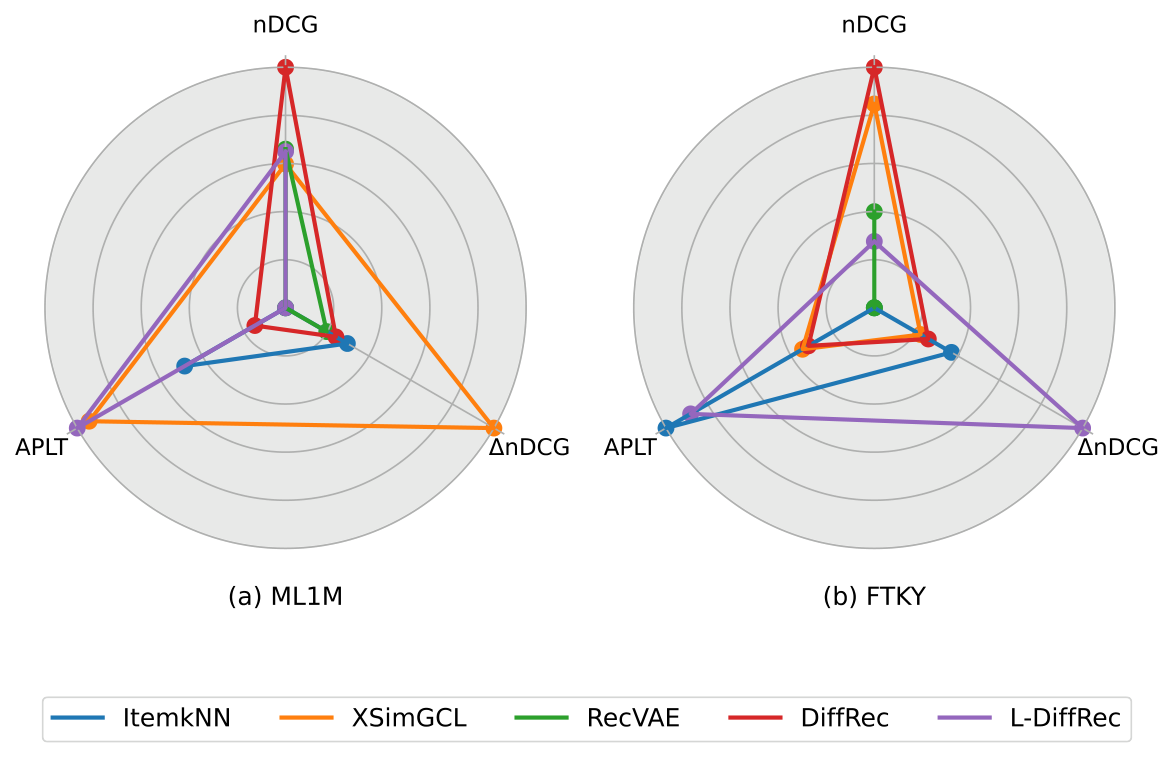
Key Findings
- Gender fairness: DiffRec shows comparable or slightly better fairness than GNN-based models
- Age fairness: More significant disparities observed, with younger users receiving better recommendations
- Provider fairness: Diffusion models favor popular items similar to other neural approaches
Key insight: Diffusion recommender models are not inherently fairer than traditional approaches. Fairness considerations should be explicitly incorporated into diffusion-based recommendation pipelines.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{malitesta2025fairdiffrec,
author = {Malitesta, Daniele and Medda, Giacomo and Purificato, Erasmo and Marras, Mirko and Malliaros, Fragkiskos D. and Boratto, Ludovico},
title = {How Fair is Your Diffusion Recommender Model?},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 19th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems},
series = {RecSys '25},
year = {2025},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
doi = {10.1145/3705328.3759318}
}